Elizabeth Holmes, the once-celebrated founder of Theranos, has been at the center of numerous debates, including speculation about whether she might be on the autism spectrum. This topic has sparked significant interest, as it delves into the intersection of leadership, neurodiversity, and public perception. In this article, we will explore the claims, evidence, and expert opinions surrounding this question, providing a comprehensive analysis for readers.
As one of the most polarizing figures in recent business history, Elizabeth Holmes has faced scrutiny not only for her role in the Theranos scandal but also for her unique personality traits. Some observers have suggested that her behavior might align with characteristics commonly associated with autism. This article aims to shed light on this complex issue, examining the evidence and offering insights into the broader implications of neurodiversity in leadership roles.
Understanding whether Elizabeth Holmes is on the autism spectrum goes beyond mere speculation. It raises important questions about how society perceives and accommodates neurodiverse individuals, especially in high-pressure environments like the corporate world. Let’s delve deeper into the details and explore the various perspectives surrounding this topic.
Read also:Leonardo Nam The Rising Star In Hollywood
Table of Contents
- Biography of Elizabeth Holmes
- What Is the Autism Spectrum?
- Traits and Behaviors Linked to Autism
- Analyzing Elizabeth Holmes' Behavior
- Expert Opinions on Holmes and Autism
- Scientific Evidence and Research
- Neurodiversity in Leadership
- Challenging Stereotypes About Autism
- The Societal Impact of Neurodiversity
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Biography of Elizabeth Holmes
Early Life and Education
Elizabeth Holmes was born on February 4, 1984, in Washington, D.C., to a family with a strong background in public service. Her father worked for the U.S. government, while her mother was an engineer. From a young age, Holmes demonstrated a keen interest in science and innovation, which eventually led her to enroll at Stanford University at the age of 19.
Founding Theranos
During her time at Stanford, Holmes dropped out to pursue her vision of revolutionizing healthcare through blood testing technology. She founded Theranos in 2003, promising a breakthrough in diagnostic testing that would allow patients to receive accurate results from just a few drops of blood. Initially hailed as a genius entrepreneur, Holmes quickly became one of the youngest self-made female billionaires in the world.
Biodata of Elizabeth Holmes
| Full Name | Elizabeth Anne Holmes |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | February 4, 1984 |
| Place of Birth | Washington, D.C., USA |
| Education | Stanford University (dropped out) |
| Profession | Entrepreneur, CEO (formerly of Theranos) |
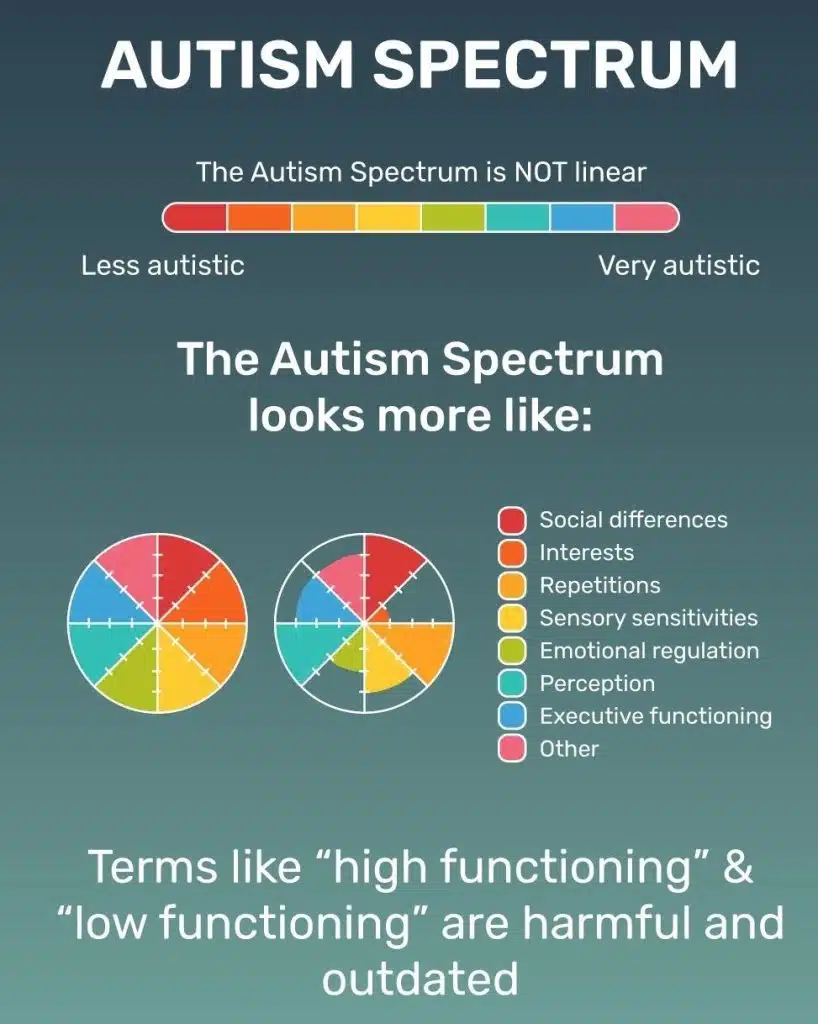
What Is the Autism Spectrum?
The autism spectrum refers to a range of neurodevelopmental conditions characterized by differences in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Individuals on the spectrum may exhibit unique strengths and challenges, making it a highly diverse and complex condition. While some people with autism experience significant difficulties in daily life, others may thrive in specific environments, particularly those that value analytical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Key Characteristics of Autism
- Difficulty with social interactions
- Repetitive behaviors or routines
- Heightened sensory sensitivities
- Exceptional focus and attention to detail
- Strong pattern recognition abilities
Traits and Behaviors Linked to Autism
Individuals on the autism spectrum often display specific traits that set them apart from neurotypical individuals. These traits can include intense focus on particular subjects, difficulty interpreting nonverbal cues, and a preference for structured environments. While these characteristics can pose challenges in certain situations, they also offer distinct advantages in fields requiring precision and innovation.
Common Behavioral Patterns
- Monotone speech or lack of emotional expression
- Avoidance of eye contact during conversations
- Preference for logical reasoning over emotional responses
- Strong adherence to rules and routines
Analyzing Elizabeth Holmes' Behavior
Elizabeth Holmes has been described by many as having a distinctive communication style, characterized by a monotone voice, minimal facial expressions, and a tendency to avoid eye contact. These traits have led some observers to speculate about her potential placement on the autism spectrum. However, it is essential to approach such claims with caution, as they often rely on anecdotal evidence rather than scientific assessment.
Key Observations
- Monotone speech patterns during public appearances
- Consistent use of scripted language in interviews
- Limited engagement with emotional topics
Expert Opinions on Holmes and Autism
Experts in the field of autism have weighed in on the possibility of Elizabeth Holmes being on the spectrum. While some psychologists suggest that her behavior aligns with certain autistic traits, others caution against diagnosing public figures without direct evaluation. The lack of concrete evidence makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions.
Read also:Sophia Ali A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Insights from Psychologists
Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in neurodiversity, notes that "while Elizabeth Holmes exhibits some behaviors commonly associated with autism, it is crucial to remember that these traits can also be influenced by other factors, such as personality type or learned behaviors."
Scientific Evidence and Research
Research into autism spectrum disorders has advanced significantly in recent years, providing valuable insights into the condition's complexities. Studies have shown that individuals on the spectrum often possess unique cognitive abilities, which can be advantageous in certain professions. However, the absence of a universally accepted diagnostic tool means that assessments remain subjective to some extent.
Key Findings
- Autistic individuals often excel in fields requiring analytical skills
- Neurodiversity can enhance creativity and innovation
- Early intervention and support are critical for success
Neurodiversity in Leadership
The concept of neurodiversity challenges traditional notions of leadership by emphasizing the value of diverse perspectives. Many successful leaders, including those on the autism spectrum, bring unique strengths to their roles, such as exceptional attention to detail and a strong work ethic. By embracing neurodiversity, organizations can foster more inclusive and innovative environments.
Benefits of Neurodiverse Leadership
- Enhanced problem-solving capabilities
- Improved decision-making through diverse viewpoints
- Increased adaptability in dynamic environments
Challenging Stereotypes About Autism
Stereotypes about autism can perpetuate misunderstandings and hinder progress toward greater inclusion. It is vital to recognize that individuals on the spectrum are as diverse as any other group, possessing a wide range of abilities and interests. By challenging these stereotypes, society can create more equitable opportunities for all.
Common Misconceptions
- Autistic individuals lack empathy
- All people with autism have intellectual disabilities
- Autism is a barrier to success in leadership roles
The Societal Impact of Neurodiversity
As awareness of neurodiversity grows, so does the potential for positive societal change. By embracing the strengths and contributions of neurodiverse individuals, communities can benefit from increased innovation and creativity. This shift in perspective also encourages greater acceptance and understanding of differences, fostering a more inclusive world.
Steps Toward Inclusion
- Promoting education and awareness about neurodiversity
- Encouraging businesses to hire neurodiverse talent
- Supporting research into autism spectrum disorders
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the question of whether Elizabeth Holmes is on the autism spectrum remains open to interpretation. While certain aspects of her behavior align with autistic traits, it is essential to approach such claims with scientific rigor and respect for individual privacy. By fostering greater understanding of neurodiversity, society can better appreciate the contributions of all individuals, regardless of their neurological profiles.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site that delve into topics related to leadership, neurodiversity, and personal development. Together, we can continue the conversation and work toward a more inclusive future.